To illustrate how to use synon2hbm, here's how you can create a small Synon model, and use synon2hbm to generate java classes to access it.
This guide will tell you how to:
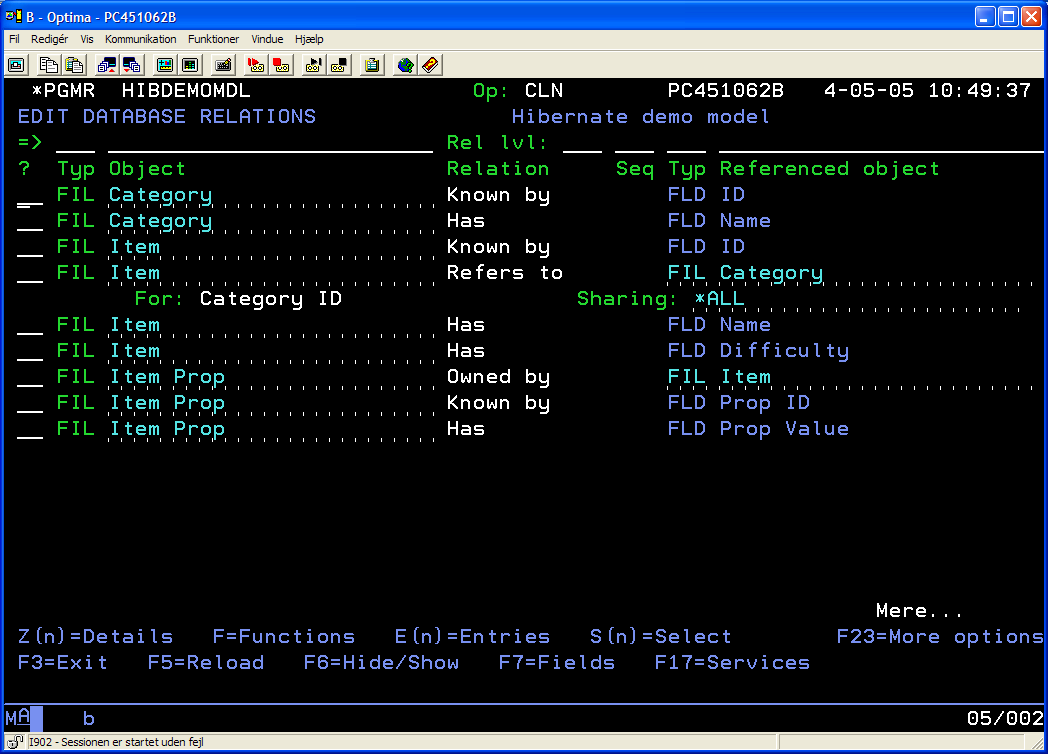
First, create a Synon model as illustrated by the following screendumps.
Define the database entities and relations as follows:

Define the fields like this:
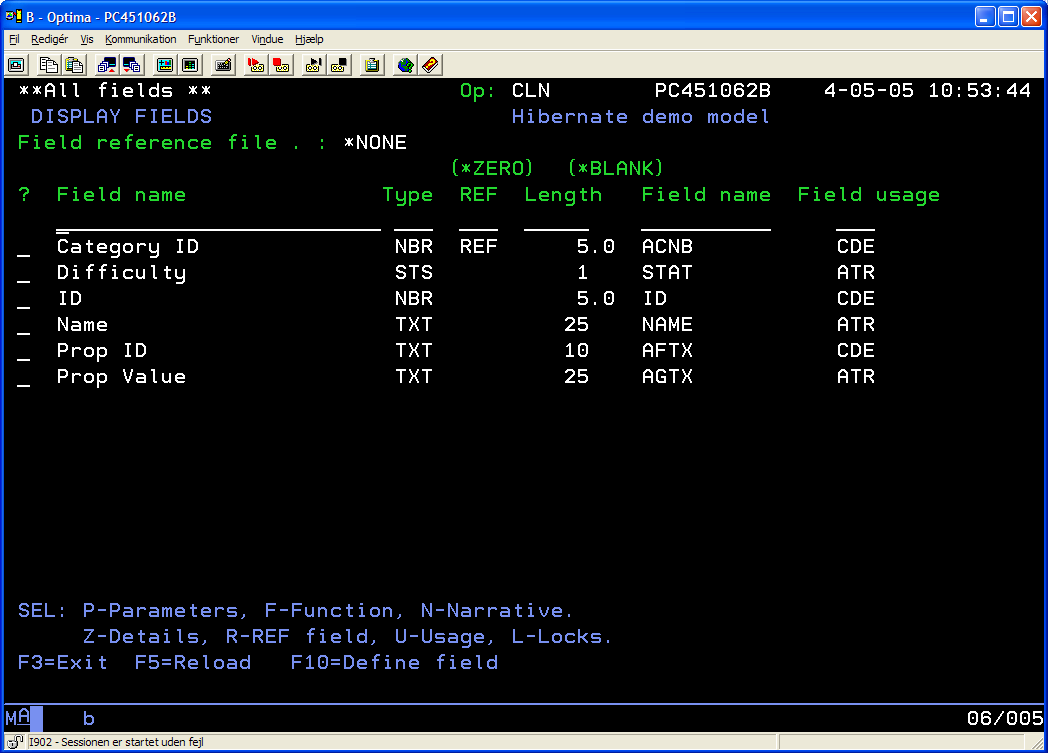
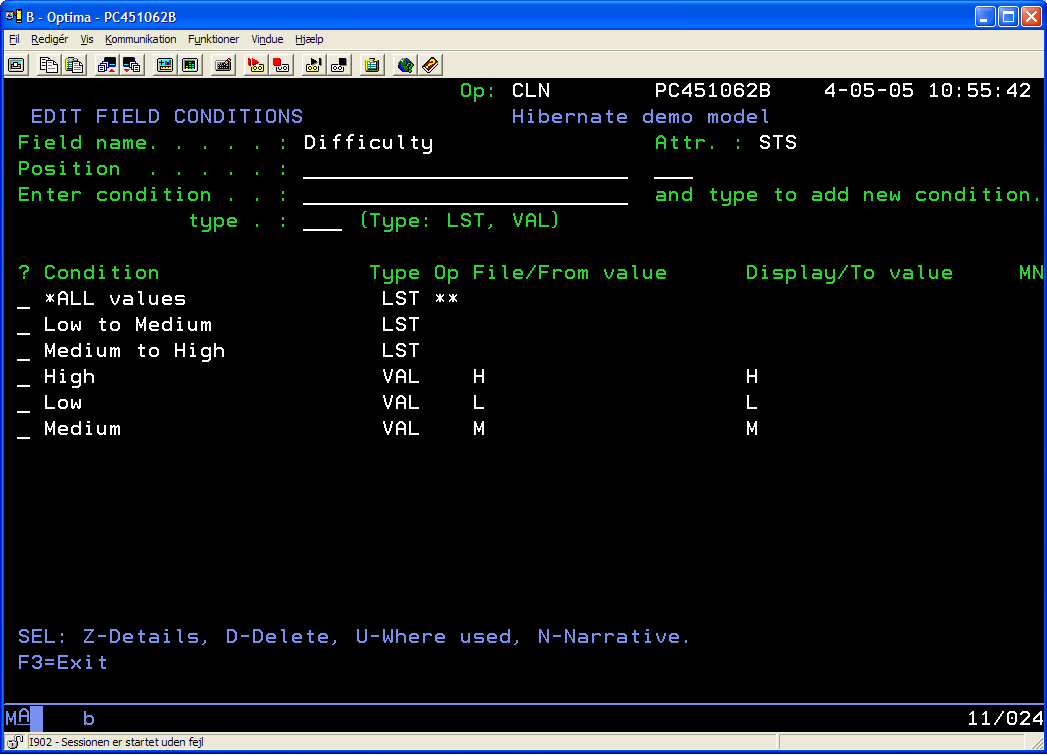
Add some conditions for the Difficulty field. The "Medium to High" condition list is used
in one of the test cases, so you should add a condition list with that name. Other than that,
their names are not important,
but create both a few condition values and some condition lists.
You can also add narratives for conditions, fields and tables.
If you do, they will be used for javadoc comments.
It is not required to run the generator, but if you
want to run the dao tests (the integrationtest target in the buildscript),
you must start journaling on the files using these commands:
synon2hbm looks for 2 access path names: Hibernate and .Hibernate (dot Hibernate).
For files which have an access path named .Hibernate, synon2hbm generates java classes
for all the fields used in the file. For files whith an access path named Hibernate
(without the dot), synon2hbm does the same and generates Hibernate mappings
or the file.
The .Hibernate access path is usefull if you want to maintain your hibernate mappings
manually, but here we want synon2hbm to generate the Hibernate mappings for us,
so add an access path called Hibernate on each file.
Download and unpack synon2hbm, or check out the synon2hbm module from cvs. Run the ant buildscript.
| CCSID | Prefix |
|---|---|
| 500 (International/latin) | @@ |
| 037 (US) | @@ |
| 277 (Danish) | ØØ |
| 273 (German) | §§ |